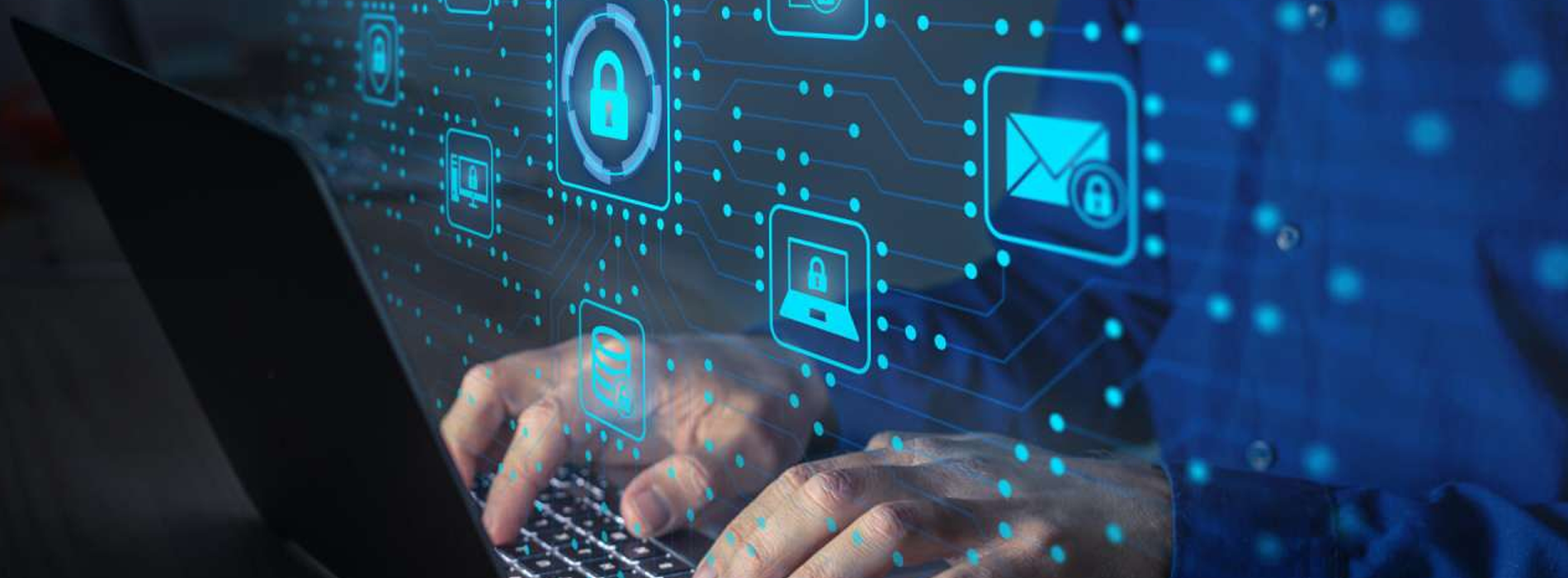
In today’s digital landscape, website security is not just an optional feature; it’s a necessity. With cyberattacks becoming more sophisticated, protecting your website from potential breaches is critical. A single vulnerability can lead to loss of sensitive data, financial repercussions, and even reputational damage. In this guide, we’ll explore expert tips to fortify your website against security threats and keep it running smoothly.
1. Understanding the Importance of Website Security
Before diving into the specifics, let’s clarify why website security is crucial. Your website is often the first point of contact between your brand and customers. A breach can compromise user trust, expose sensitive information, and impact SEO rankings. Additionally, search engines like Google penalize sites that are flagged as unsafe.
2. Common Website Security Threats
Knowing the potential threats is the first step toward securing your website. Here are some of the most common issues:
- Malware Attacks: Malicious software designed to harm or exploit systems.
- Phishing Scams: Fake websites that trick users into revealing sensitive data.
- SQL Injections: Exploiting vulnerabilities in a database to gain access to data.
- DDoS Attacks: Overloading a server to make a website unavailable.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Injecting malicious scripts into trusted websites.
3. Keep Your Software Up-to-Date
Outdated software is one of the leading causes of website vulnerabilities. Regularly update:
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Platforms like WordPress often release patches to fix vulnerabilities.
- Plugins and Themes: Ensure all third-party extensions are up-to-date.
- Server Software: Check with your hosting provider for the latest server updates.
4. Use Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication
Weak passwords are an open invitation for hackers. To secure your website:
- Create strong passwords: Combine uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols.
- Avoid reuse: Never use the same password across multiple platforms.
- Implement two-factor authentication (2FA): Adds an extra layer of security by requiring a secondary verification method.
5. Install an SSL Certificate
An SSL certificate encrypts data transferred between a user’s browser and your website, making it harder for hackers to intercept sensitive information. Websites with SSL certificates display a padlock icon and “https” in the URL, which also boosts SEO rankings.
6. Regularly Back Up Your Website
In case of a breach, a backup ensures that you can restore your website to its previous state. Follow these backup tips:
- Automate backups: Use tools to schedule regular backups.
- Store backups securely: Use cloud storage or offline locations.
- Test your backups: Regularly verify that your backup files are functional.
7. Implement a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A Web Application Firewall acts as a shield between your website and potential threats. It monitors and filters malicious traffic while allowing legitimate users to access your site. Popular WAF solutions include Cloudflare, Sucuri, and Imperva.
8. Monitor Your Website Activity
Keeping an eye on your website can help you detect unusual activities before they escalate. Use tools like:
- Google Search Console: Monitor search performance and potential security issues.
- Security Plugins: Install plugins like Wordfence or iThemes Security for real-time monitoring.
- Log Analysis: Review access logs to identify unauthorized attempts.
9. Restrict User Access
Not everyone needs full access to your website. Limit permissions based on roles:
- Administrator access: Only trusted personnel should have admin rights.
- Role-based access: Assign specific permissions to users based on their responsibilities.
- Deactivate inactive accounts: Remove access for users no longer involved with the website.
10. Protect Against SQL Injections
SQL injections are a common hacking technique used to manipulate databases. Here’s how to protect against them:
- Use parameterized queries: Avoid directly including user input in SQL statements.
- Sanitize inputs: Clean all user inputs to prevent malicious code.
- Implement a firewall: A WAF can help block injection attempts.
11. Regularly Scan for Malware
Malware can infiltrate your website unnoticed and cause significant damage. Use tools like:
- Sucuri SiteCheck: Free malware scanning and monitoring.
- MalCare: Comprehensive malware detection and removal for WordPress sites.
- Norton Safe Web: Check for vulnerabilities and malicious content.
12. Educate Your Team
Your team plays a vital role in maintaining website security. Conduct regular training to:
- Recognize phishing attempts.
- Follow best practices for secure login.
- Handle sensitive information responsibly.
13. Choose a Secure Hosting Provider
Your hosting provider is your first line of defense against attacks. Look for:
- Built-in security features: Firewalls, malware scanning, and DDoS protection.
- Regular updates: A provider that actively patches server vulnerabilities.
- Reliable customer support: For quick assistance in case of a breach.
14. Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
A CDN not only improves website speed but also enhances security. It does this by:
- Distributing traffic: Preventing server overload during DDoS attacks.
- Blocking threats: Filtering malicious traffic before it reaches your site.
15. Test Your Website Regularly
Conduct regular penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities. Hire professionals to simulate attacks and suggest improvements. Testing ensures your security measures remain effective against evolving threats.
Conclusion: Stay Vigilant, Stay Secure
Website security is a continuous process that demands vigilance and proactive measures. By following these expert tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches and protect your brand’s reputation. Remember, a secure website builds trust, improves user experience, and enhances your SEO rankings. Take action today to fortify your digital presence!